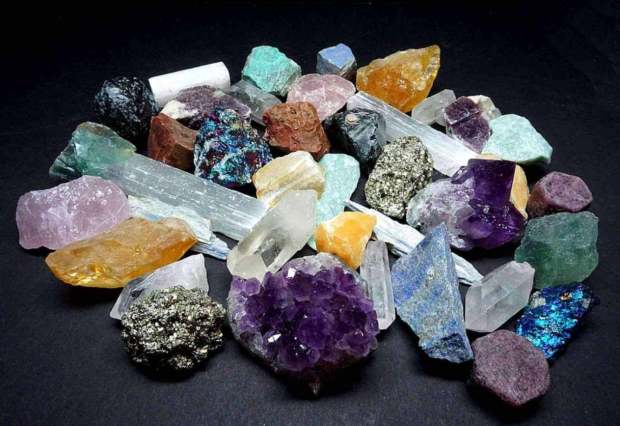
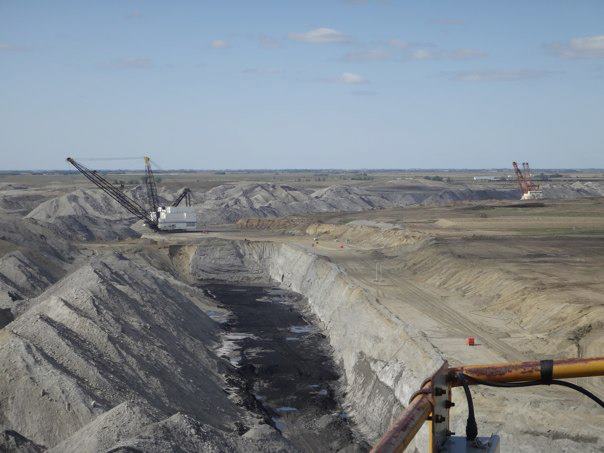
EC7.3 Investigate the characteristics and formation of the surface geology of Saskatchewan, including soil, and identify correlations between surface geology and past, present, and possible future land uses.
Surface Geology




How Has/Will Surface Geology Changed in Our Community?
Homework: Make a three-column table in your science duo tang with the main title as “Changing Places.” The first column as “Past”, second column as “Present” and third column as “Future Possibility.” Ask your parents to help you fill in what they know, from what they have in seen in our community or in another one that they have lived in.
Example:
Past: Present: Future Possibility:
Civic Auditorium Empty space Sports center
Pasture land by hospital New housing Housing and more businesses
Farmers Fields Land for mining Back to farming land
Positive and Negative Effects of Development

Brainstorm with a group of 3-4 people:
*Think of the environment, people, and the economy while answering.
What are the positive and negative effects of housing development?
p.617 of teacher guide
Pick a Product

Photo by Oleg Magni on Pexels.com
Material development means that we are producing more and more and more and more. We need to think about if we need it, why we are purchasing it and if we should support its creation. We need to ask the hard questions.
- Is it creating pollution?
- How do I get rid of it after I am done using it? Can it be recycled? Where does it go?
- Can I be using something else to save waste? Is there a better solution?
YOUR TASK:
- Pick a common, everyday product you use daily with your group of 2-3 people.
- Find out and make a list of what materials are used to make the product.
- Find out how those materials are made and where each material and its ingredients come from. (Make a note if transportation is needed during the making of the material).
- Answer these questions:
- What kind of packaging is used? Make sure to include this in your material list.
- Look at the minerals used to make the materials in your product. What are the impacts on the environment from mining these minerals?
- How does the product get to you? What does that do to the environment?
- How do you get rid of it after you are done using it? Can it be recycled? Where does it go? Where does the garbage go? Does this garbage have an effect on the landscape?
- Can you suggest any changes that could be made to the product to reduce its impact on the environment?
- Are you going to keep using it or make any changes?
USE YOUR GROUPS STRENGTHS TO MAKE A PRESENTATION ABOUT YOUR PRODUCT.